作为程序员,理解ECF很重要,这有一些原因:
- 理解重要的系统概念
- 理解应用程序是如何与操作系统交互的
- 帮助你编写有趣的新应用程序
- 理解并发
异常
异常是异常控制流的一部分,它一部分由硬件实现,一部分由操作系统实现
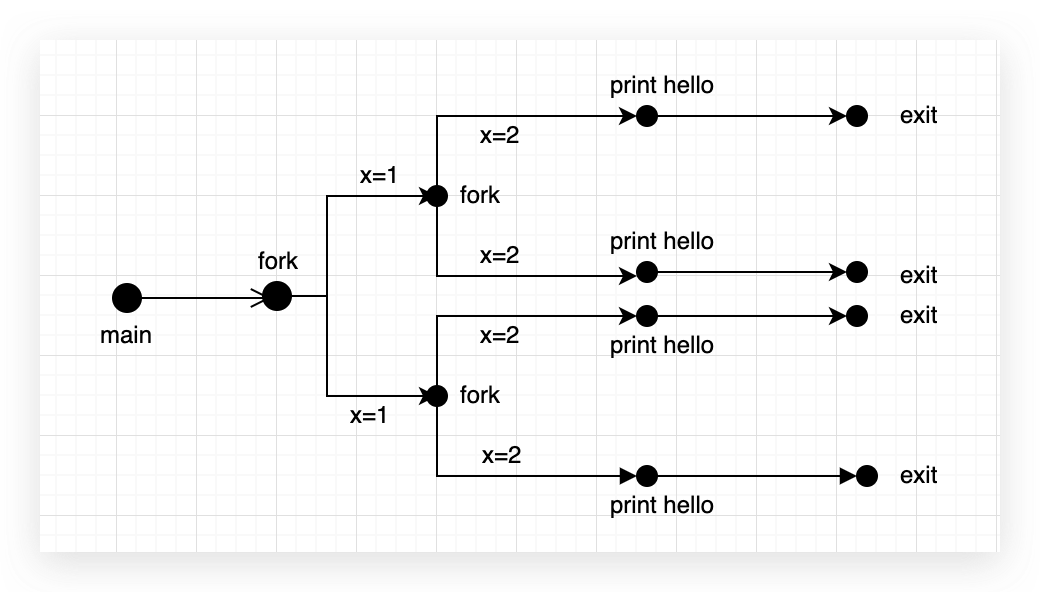
8.11
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| #include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int i;
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
fork();
printf("hello\n");
exit(0);
}
|
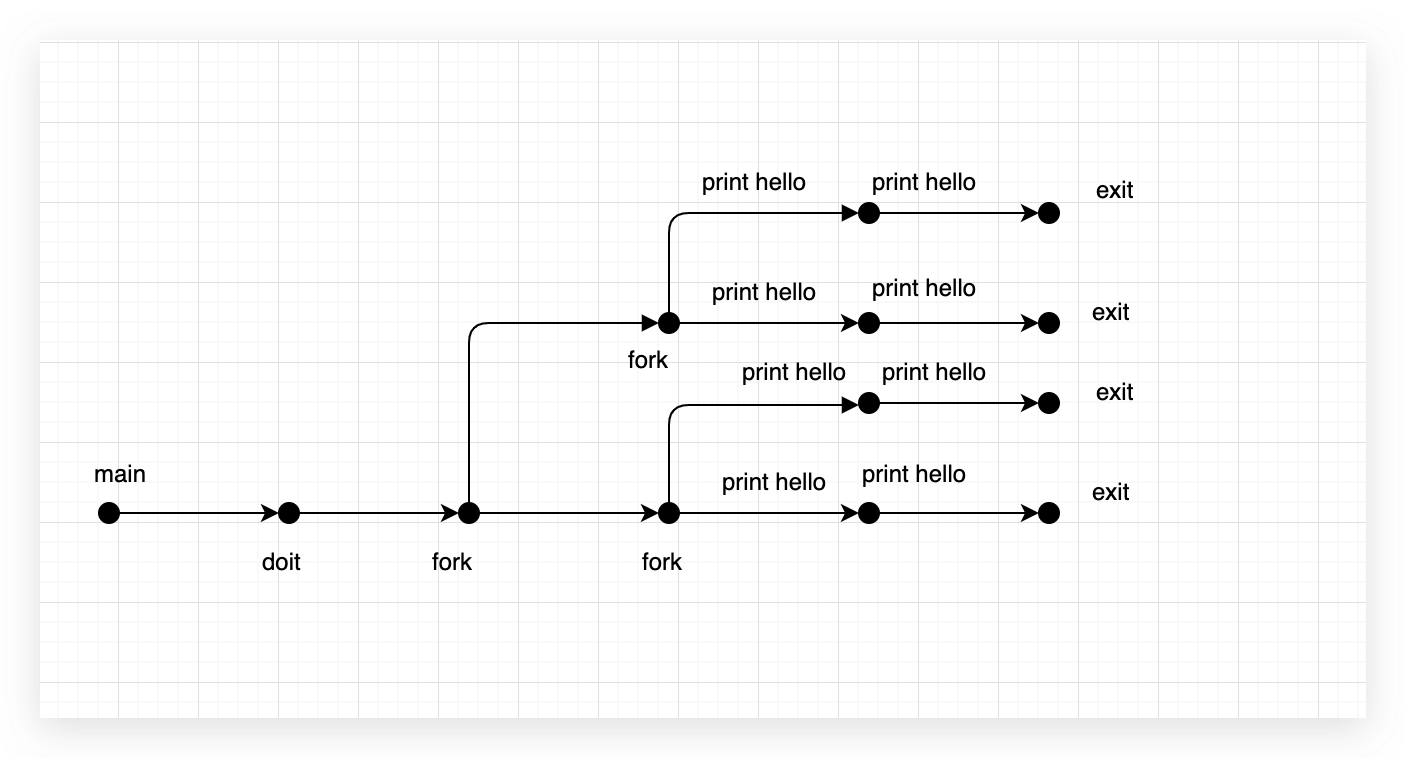
8.12
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void doit(){
fork();
fork();
printf("hello\n");
return;
}
int main(){
doit();
printf("hello\n");
exit(0);
}
|
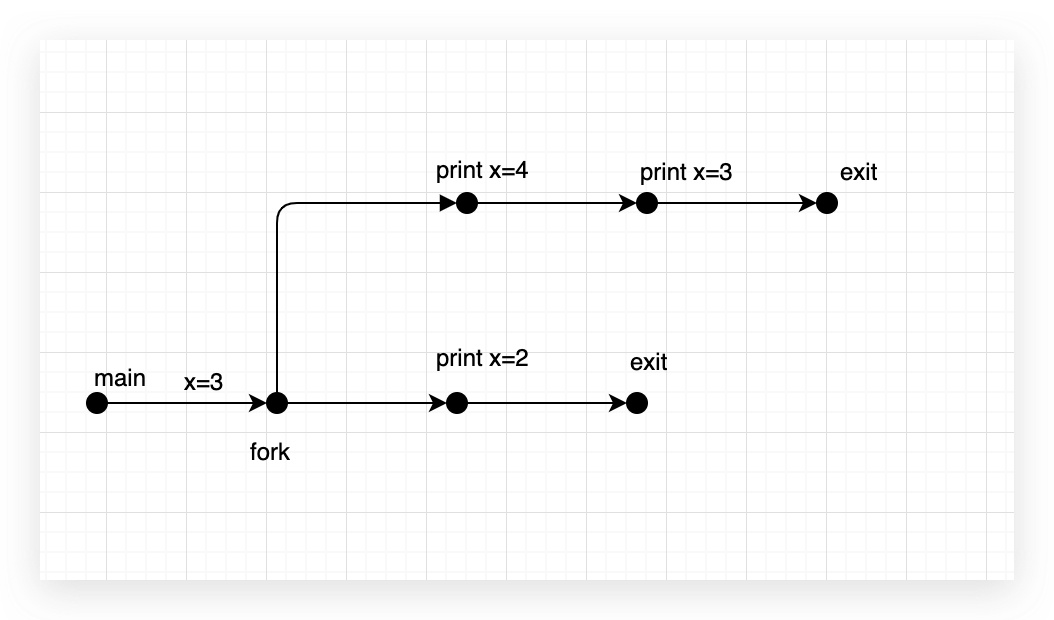
8.13
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(){
int x = 3;
if(fork() != 0)
printf("x=%d\n",++x);
printf("x=%d\n",--x);
exit(0);
}
|
8.14
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void doit(){
if(fork() == 0){
fork();
printf("hello\n");
exit(0);
}
return;
}
int main(){
doit();
printf("hello\n");
exit(0);
}
|
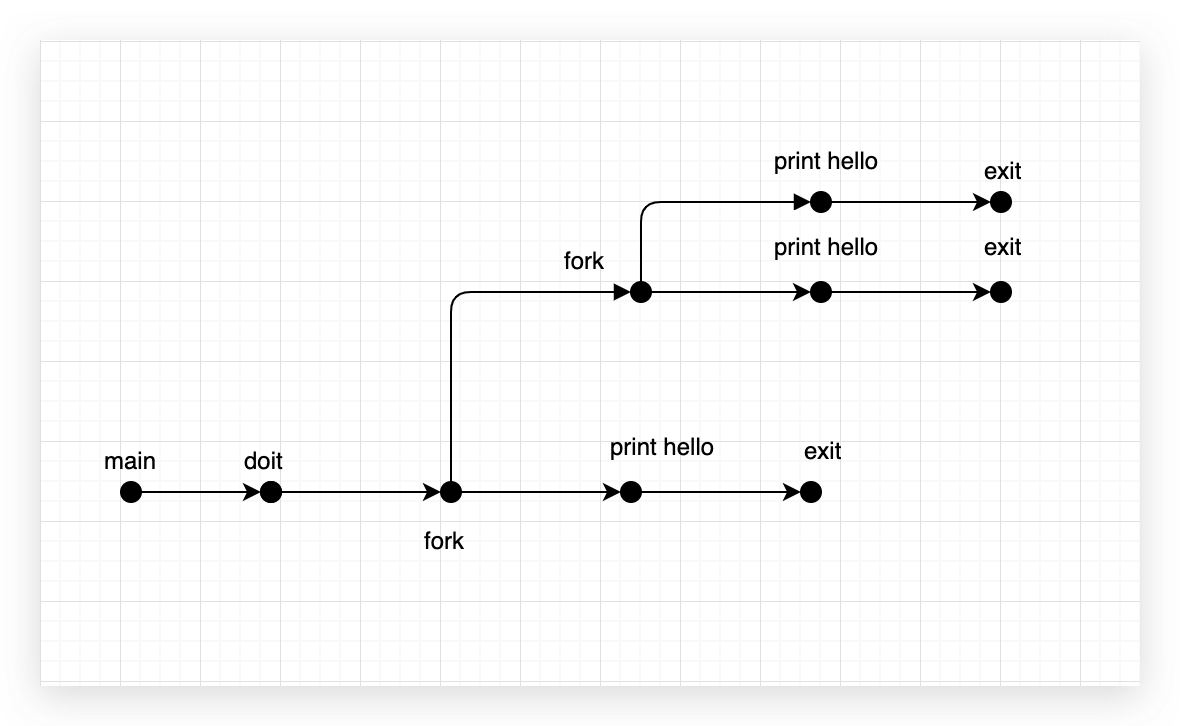
8.15
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void doit(){
if(fork()==0){
fork();
printf("hello\n");
return;
}
return;
}
int main(){
doit();
printf("hello\n");
exit(0);
}
|

8.16
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int counter = 1;
int main(){
if(fork()==0){
counter++;
exit(0);
} else {
wait(NULL);
printf("couter = %d\n",++counter);
}
exit(0);
}
|
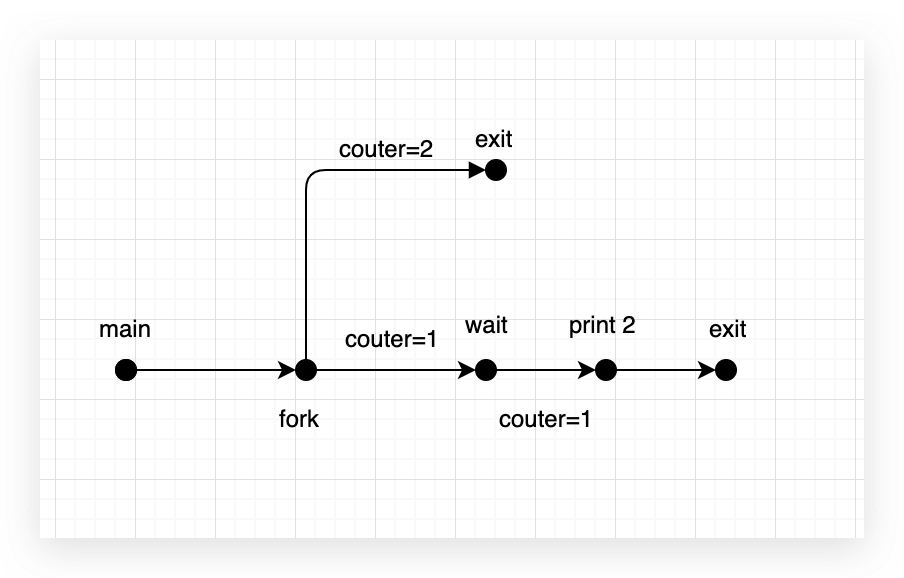
8.18
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void end(){
printf("2");
fflush(stdout);
}
int main(){
if(fork()==0)
atexit(end);
if(fork()==0) {
printf("0");
fflush(stdout);
} else {
printf(1);
fflush(stdout);
}
exit(0);
}
|
8.19
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void foo(int n){
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
fork();
printf("hello\n");
exit(0);
}
int main(){
foo(4);
return 0;
}
|
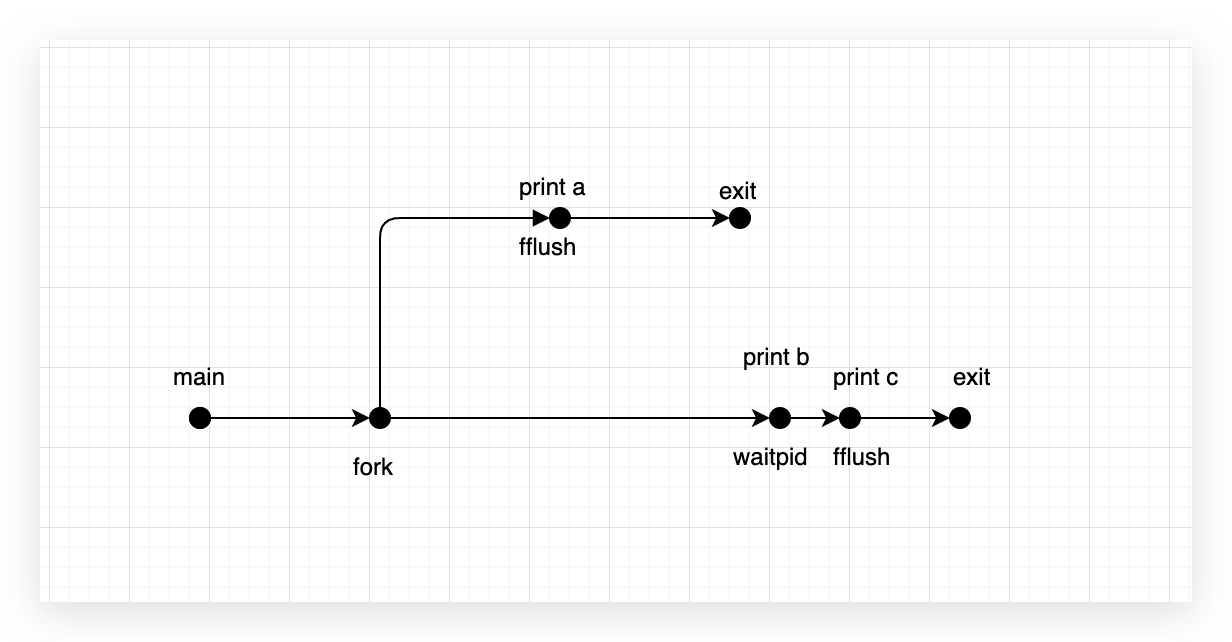
8.21
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(){
if(fork()==0){
printf("a");
fflush(stdout);
exit(0);
} else {
printf("b");
waitpid(-1,NULL,0);
}
printf("c");
fflush(stdout);
exit(0);
}
|